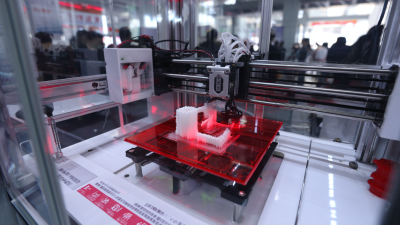
In recent years, the manufacturing landscape has undergone a significant transformation, largely driven by technological advancements. One of the most groundbreaking innovations reshaping this sector is rapid 3D printing. This technique not only accelerates production processes but also enhances design flexibility and innovation. By allowing for the quick creation of prototypes and end-use products directly from digital files, rapid 3D printing enables manufacturers to respond swiftly to market demands and customize products to meet specific consumer needs.
As industries increasingly adopt rapid 3D printing, the implications for efficiency and sustainability are profound. Traditional manufacturing methods often involve lengthy production cycles and substantial material waste. In contrast, rapid 3D printing minimizes these concerns by using additive processes, where materials are added layer by layer, resulting in reduced scrap and energy consumption. This shift not only fosters a more agile manufacturing approach but also contributes to environmental sustainability, a crucial consideration in today's economy. Ultimately, rapid 3D printing is not just a fleeting trend; it represents a pivotal shift towards a more responsive, resource-efficient manufacturing future.

Rapid 3D printing is an innovative manufacturing process that enables the quick production of complex parts and products directly from digital models. This technology employs various printing techniques, such as fused deposition modeling (FDM), stereolithography (SLA), and selective laser sintering (SLS), to build objects layer by layer. With the ability to reduce lead times significantly, rapid 3D printing has transformed traditional manufacturing, allowing for faster prototyping, customization, and lower material waste.
One of the key advantages of rapid 3D printing is its capacity for creating intricate designs that may be challenging or impossible to achieve with conventional manufacturing methods. This opens up new possibilities in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare, where customized components are often required. Additionally, rapid 3D printing allows for iterations and modifications to be made quickly, enabling designers and engineers to refine their ideas without the lengthy delays typically experienced in traditional production methods.
Tips: When considering rapid 3D printing for your projects, be mindful of the material you choose, as it can greatly affect the final product's strength and durability. Additionally, collaborate closely with your design team to ensure that your digital model is optimized for the printing process, reducing the potential for errors and ensuring the best possible outcome. Lastly, always keep scalability in mind; while rapid 3D printing is fantastic for prototyping, assess whether you have a plan in place for larger production runs if needed in the future.
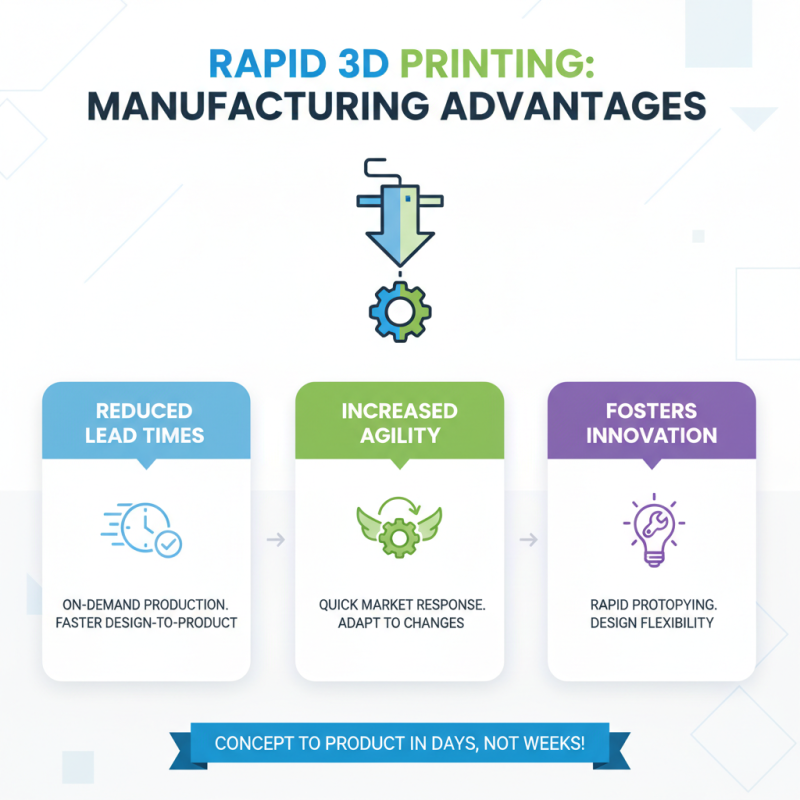
Rapid 3D printing has emerged as a pivotal technology in modern manufacturing, offering significant advantages that streamline production processes. One of the key benefits is the reduction of lead times. Traditional manufacturing often involves lengthy setup and production schedules, whereas rapid 3D printing enables companies to design and produce parts on demand, drastically shortening the time from concept to final product. This agility allows businesses to respond quickly to market demands and changes, fostering innovation and flexibility.
Another major advantage is the ability to create complex geometries and custom designs with ease. Traditional methods may limit the design possibilities due to constraints in machining and tooling. In contrast, 3D printing allows for intricate designs that can optimize performance and reduce material waste. This capability not only enhances the functionality of components but also supports sustainable manufacturing practices by minimizing excess material usage. As a result, rapid 3D printing is not only transforming the manufacturing landscape but also paving the way for more efficient and environmentally friendly processes.
Rapid 3D printing has emerged as a pivotal technology across various industries, revolutionizing traditional manufacturing processes. One of the most significant applications is in the aerospace sector, where lightweight and complex parts are crucial for enhancing fuel efficiency and performance. According to a report by the consulting firm PwC, approximately 25% of aerospace companies are already utilizing 3D printing for production, specifically for parts such as brackets and air ducts. This method not only reduces material waste but also expedites the prototyping phase, allowing for faster iterations and innovations in design.
In the healthcare industry, rapid 3D printing is making strides in personalized medical solutions. Surgeons now rely on 3D-printed models to better understand patient anatomies before complex procedures, significantly improving surgical outcomes. A study from Wohlers Associates has shown that the medical 3D printing market is expected to reach $6.1 billion by 2026, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 23% from 2021. Furthermore, the creation of customized implants and prosthetics tailored to individual patients underscores how rapid 3D printing not only enhances patient care but also streamlines production timelines and costs.
The automotive industry is also leveraging rapid 3D printing to produce functional prototypes and low-volume production parts. Reports indicate that around 33% of automobile manufacturers plan to adopt 3D printing technologies for production parts within the next few years. This shift towards additive manufacturing allows for the creation of intricate geometries that traditional methods cannot achieve, resulting in more efficient designs and reduced lead times. As the potential of rapid 3D printing unfolds, its applications across these industries highlight a transformational shift in how products are designed and manufactured.
| Industry | Applications | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Production of lightweight components | Reduced weight and improved fuel efficiency | Regulatory certifications |
| Automotive | Rapid prototyping of parts | Faster time to market | Material limitations |
| Medical | Custom prosthetics and implants | Personalized patient care | Post-production treatment requirements |
| Consumer Goods | Customized products | Enhanced user experience | Cost of production in small batches |
| Construction | 3D printed structures | Reduced labor and material waste | Durability concerns |
Rapid 3D printing is revolutionizing manufacturing by enabling faster prototyping and production of complex parts. However, its implementation is not without challenges. One significant limitation is the disparity in material properties when comparing 3D printed parts to traditionally manufactured components. Achieving the desired strength, durability, and surface finish can be difficult, posing potential risks in applications where performance is critical. Additionally, the technology requires skilled personnel who understand both the software and hardware intricacies, which can lead to a shortage of qualified operators.
Another challenge lies in the scalability of production. While rapid 3D printing excels at creating small batches or unique designs, transitioning to large-scale manufacturing can be problematic. The time and cost of printing large objects can diminish the economical advantages that 3D printing typically offers. Companies must also navigate the complexities of integrating advanced 3D printing systems with existing manufacturing processes, necessitating a thorough redesign of workflows.
Tips for companies considering rapid 3D printing include conducting a thorough assessment of their specific needs before implementation, investing in training for personnel to maximize the technology’s potential, and starting with smaller, manageable projects to build expertise. Businesses should also remain aware of the evolving landscape of materials and techniques in 3D printing, as innovation is rapidly reshaping what is possible, paving the way for more efficient processes and applications in the future.
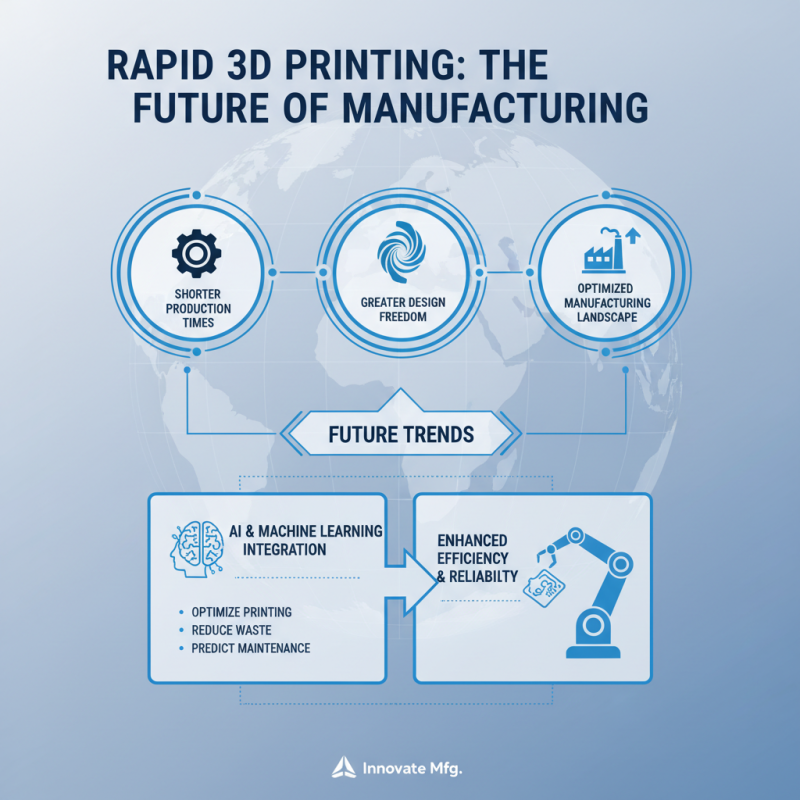
Rapid 3D printing is reshaping the manufacturing landscape by enabling shorter production times and greater design freedom. As technology advances, we can expect several future trends to emerge within the manufacturing sector. One significant trend is the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into 3D printing processes. These technologies will optimize printing parameters, reduce waste, and predict when maintenance is needed, thus improving efficiency and reliability.
Another key trend is the sustained movement towards sustainable materials and eco-friendly practices in rapid 3D printing. As industries become more conscious of their environmental impact, manufacturers will increasingly utilize recyclable and biodegradable materials for production. This shift not only reduces carbon footprints but also aligns with changing consumer preferences for sustainable products. Additionally, the incorporation of circular economy principles into manufacturing processes will enable the reuse and repurposing of printed materials, further enhancing sustainability in the sector.
Collaboration and customization are also set to rise in prominence. The ability to create tailored solutions quickly allows manufacturers to respond to specific customer needs with agility. As businesses increasingly move towards on-demand production, the traditional mass production model is evolving, making way for a more personalized approach that caters to individual preferences and requirements. This evolution will not only enhance customer satisfaction but also lead to innovative products that can redefine market standards.