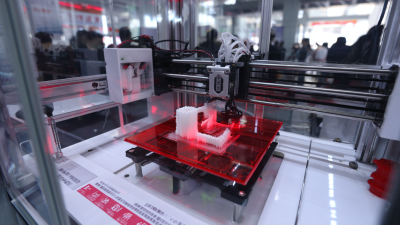
In the rapidly evolving landscape of product development, "rapid prototyping 3D printing" has emerged as a transformative technology, enabling designers and engineers to bring their ideas to life faster and more efficiently than ever before. Renowned expert in additive manufacturing, Dr. Emily Turner, emphasizes the significance of this technology, stating, "Rapid prototyping 3D printing is not just about speed; it's about empowering innovation by allowing for quicker iterations and real-time feedback." Such insights capture the essence of how this technique is revolutionizing the design process across various industries.
The ability to create prototypes in a matter of hours, rather than weeks, drastically shortens the product development cycle. This agility not only enhances creativity but also reduces costs associated with traditional manufacturing methods. As businesses strive to stay competitive, harnessing the power of rapid prototyping 3D printing can be a game-changer, facilitating a more dynamic approach to product design.
In this guide, we will explore essential tips and strategies for leveraging rapid prototyping 3D printing effectively, ensuring that designers can make the most of this groundbreaking technology. Whether you are new to the field or looking to refine your existing practices, understanding the nuances of rapid prototyping 3D printing will equip you to navigate the challenges and opportunities of modern product development.

Rapid prototyping is a pivotal component in the design process, enabling creators to transform ideas into tangible models swiftly. This technique facilitates the exploration of concepts and iterations, allowing designers to examine the physical form, functionality, and ergonomics of their creations. By employing 3D printing, designers can produce prototypes in a fraction of the time compared to traditional methods, effectively reducing development cycles. This accelerated pace not only fosters innovation but also allows for more comprehensive testing and refinement before final production.
Moreover, rapid prototyping plays an essential role in enhancing communication among teams and stakeholders. With 3D printed models, designers can present their ideas visually and physically, making abstract concepts more accessible. This tangible representation helps stakeholders understand the design's intent and usability, streamlining feedback and decision-making processes. Furthermore, early identification of potential design flaws through prototypes minimizes costly revisions later in the production phase. Ultimately, rapid prototyping with 3D printing techniques empowers designers to iterate efficiently while ensuring that the final product meets both functional and aesthetic requirements.
Rapid prototyping has revolutionized the product development process, allowing designers and engineers to create and iterate on their ideas swiftly using 3D printing techniques. According to a report from Wohlers Associates, the additive manufacturing industry is expected to reach a market value of $44.5 billion by 2025, highlighting the increasing reliance on 3D printing for effective prototyping. To harness the full potential of this technology, understanding essential 3D printing techniques is vital.
One important technique is Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), which is widely used for its cost-effectiveness and ease of use. FDM allows for rapid creation of prototypes using thermoplastic materials, making it an excellent choice for functional testing. As you prototype, remember to optimize your design by reducing complexity and incorporating features that allow for easy assembly. This will not only speed up the manufacturing process but also enhance performance testing.
Another critical technique is Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), which provides greater design freedom and produces more durable prototypes compared to FDM. SLS can handle complex geometries that are crucial for validating performance requirements in a real-world setting. When applying SLS, consider using high-quality powders and maintaining optimal print settings to achieve the best results. By integrating these techniques into your workflow, you can significantly reduce time-to-market and enhance the functionality of your prototypes.
| Technique | Material | Layer Height (mm) | Print Speed (mm/s) | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) | PLA, ABS | 0.1 - 0.3 | 50 - 100 | Functional Prototypes |
| Stereolithography (SLA) | Resin | 0.025 - 0.1 | 20 - 30 | High-Detail Models |
| Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) | Nylon, TPU | 0.1 - 0.2 | 30 - 50 | Functional Parts |
| Digital Light Processing (DLP) | Resin | 0.05 - 0.1 | 10 - 25 | Jewelry, Dental Models |
| Binder Jetting | Metal, Sand | 0.1 - 0.5 | 40 - 80 | Complex Shapes |
When embarking on a rapid prototyping journey using 3D printing techniques, selecting the right filament is crucial for achieving the desired results. Each type of filament has unique properties that cater to specific project requirements. For instance, if durability and strength are top priorities, materials like ABS or PETG might be ideal choices due to their excellent mechanical properties. On the other hand, if your project demands intricate details or a smoother surface finish, PLA could be more suitable because it is known for its ease of use and fine resolution.
It’s also important to consider the environment in which the prototype will be used. If it will face high temperatures, then filaments like nylon or ASA are preferable, as they exhibit better heat resistance. Additionally, projects that require flexibility or a rubber-like feel can benefit from elastomers such as TPU. Beyond mechanical properties, aesthetic aspects such as color and finish should also influence your filament selection. By carefully evaluating the objectives and conditions of your project, you can ensure that the chosen filament enhances the functionality and visual appeal of your 3D printed prototype.
This chart illustrates the ease of use ratings for different types of 3D printing filaments. Understanding these ratings can help you select the most appropriate material for your prototyping needs.

When engaging in rapid prototyping with 3D printing, optimizing your 3D models is vital for enhancing print quality and speed. According to a recent report by Wohlers Associates, the 3D printing industry has an annual growth rate of 25.76%, underscoring the urgency for professionals to refine their modeling strategies. Effective optimization techniques start with the delicate balance of polygon count and detail. Reducing polygons while maintaining necessary visual fidelity not only enhances the computational speed but also minimizes print time. Studies suggest that intricate models with lower polygon counts can cut down on printing time by as much as 30% without sacrificing quality, making it crucial to possess proficiency in 3D modeling software.
In addition to polygon management, the orientation of the model plays a significant role in print efficiency. Research published in the Journal of Manufacturing Processes indicates that prints oriented at optimal angles can reduce the wear on the extruder and the material used, leading to up to a 40% increase in material efficiency. This optimization allows for faster print speeds and improved surface quality, especially on intricate designs. Utilizing proper support structures and choosing the right layer height can further enhance the final output, yielding products that satisfy both aesthetic and functional demands in rapid prototyping contexts. Through implementing these strategies, designers and engineers can significantly streamline their workflow while ensuring high-quality prototypes.
Post-processing is a vital step in transforming a 3D printed prototype into a polished final product. According to a report by SmarTech Analysis, the market for post-processing technologies is expected to grow over 20% annually, indicating a significant shift towards more refined manufacturing processes. Techniques such as sanding, polishing, and chemical smoothing are essential for enhancing the surface finish and dimensional accuracy of parts, especially those produced by FDM and SLA methods. Employing these techniques effectively can reduce the visibility of layer lines and improve the overall aesthetics, which is particularly important for prototypes intended for client presentations or high-stakes projects.
Moreover, integrating proper post-processing practices can greatly impact the performance and durability of 3D printed prototypes. As highlighted in a study by Wohlers Associates, nearly 30% of companies have reported that inadequate post-processing leads to failures in prototype functionality and longevity. Techniques like vapor smoothing not only address surface issues but also help in achieving better mechanical properties by minimizing porosity. By investing in effective post-processing methods, businesses can ensure that their prototypes meet both functional and visual expectations, ultimately streamlining the product development cycle and enhancing time-to-market.